Mysql Getdatetime
Vore Action Rpg 2 Free. Note SYSDATETIME and SYSUTCDATETIME have more fractional seconds precision than GETDATE and GETUTCDATE. SYSDATETIMEOFFSET includes the system time zone offset. SYSDATETIME, SYSUTCDATETIME, and SYSDATETIMEOFFSET can be assigned to a variable of any of the date and time types. For an overview of all Transact-SQL date and time data types and functions, see. Patent Pilot Program Judges On American on this page. Syntax GETDATE ( ) Return Type datetime Remarks Transact-SQL statements can refer to GETDATE anywhere they can refer to a datetime expression. GETDATE is a nondeterministic function.
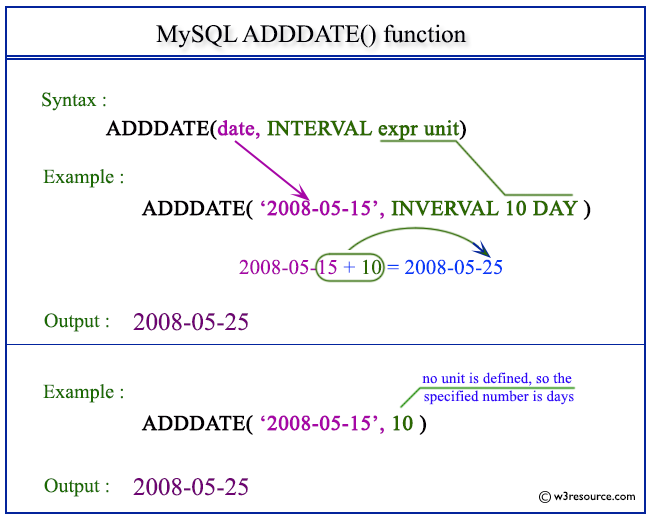
Views and expressions that reference this function in a column cannot be indexed. Using SWITCHOFFSET with the function GETDATE() can cause the query to run slowly because the query optimizer is unable to obtain accurate cardinality estimates for the GETDATE value. We recommend that you precompute the GETDATE value and then specify that value in the query as shown in the following example. In addition, use the OPTION (RECOMPILE) query hint to force the query optimizer to recompile a query plan the next time the same query is executed. The optimizer will then have accurate cardinality estimates for GETDATE() and will produce a more efficient query plan.

Sep 29, 2007 Error: Unable to convert MySQL date/time value. Unable to convert MySQL date/time value to System.DateTime at MySql.Data.Types.MySqlDateTime.GetDateTime().
DECLARE @dt datetimeoffset = switchoffset (CONVERT(datetimeoffset, GETDATE()), '-04:00'); SELECT * FROM t WHERE c1 >@dt OPTION (RECOMPILE); Examples The following examples use the six SQL Server system functions that return current date and time to return the date, time, or both. The values are returned in series; therefore, their fractional seconds might be different. Getting the current system date and time SELECT SYSDATETIME(),SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(),SYSUTCDATETIME(),CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,GETDATE(),GETUTCDATE(); Here is the result set.
SYSDATETIME() 2007-04-30 13:381 SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()2007-04-30 13:381 -07:00 SYSUTCDATETIME() 2007-04-30 20:381 CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 2007-04-30 13:10:02.047 GETDATE() 2007-04-30 13:10:02.047 GETUTCDATE() 2007-04-30 20:10:02. Psyclon Nine Divine Infekt Rar Files more. 047 B. Getting the current system date SELECT CONVERT (date, SYSDATETIME()),CONVERT (date, SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()),CONVERT (date, SYSUTCDATETIME()),CONVERT (date, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP),CONVERT (date, GETDATE()),CONVERT (date, GETUTCDATE()); Here is the result set. SYSDATETIME() 2007-05-03 SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() 2007-05-03 SYSUTCDATETIME() 2007-05-04 CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 2007-05-03 GETDATE() 2007-05-03 GETUTCDATE() 2007-05-04 C. Getting the current system time SELECT CONVERT (time, SYSDATETIME()),CONVERT (time, SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()),CONVERT (time, SYSUTCDATETIME()),CONVERT (time, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP),CONVERT (time, GETDATE()),CONVERT (time, GETUTCDATE()); Here is the result set. SYSDATETIME() 13:361 SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()13:361 SYSUTCDATETIME() 20:361 CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 13:000 GETDATE() 13:000 GETUTCDATE() 20:000 Examples: Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse The following examples use the three SQL Server system functions that return current date and time to return the date, time, or both. The values are returned in series; therefore, their fractional seconds might be different. Getting the current system date and time SELECT SYSDATETIME(),CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,GETDATE(); E.
Getting the current system date SELECT CONVERT (date, SYSDATETIME()),CONVERT (date, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP),CONVERT (date, GETDATE()); F. Getting the current system time SELECT CONVERT (time, SYSDATETIME()),CONVERT (time, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP),CONVERT (time, GETDATE()); See Also.